What are the sections of wires and cables?
Standard range of sections
There is a standard number of cross-sections of cores produced by cable manufacturers: 0.5; 0.75; 1; 1.5; 2.5; 4; 6; 10; sixteen; 25; 35; fifty; 70; 95; 120; 150; 185; 240; 300; 400; 500; 625; 800; 1000; 1200; 1600 sq. mm In this case, the maximum cross section of the conductive core can reach 6000 mm.kv. (cable КСВДСП-6000).
It is important to note that the minimum value for an aluminum cable is 2.5 mm2. This is due to the low strength of this metal, since the number of bends before the moment of refraction is much less than that of copper, that is, it can easily break at the points of attachment, during installation.
Good to know
For private houses and apartments where a linear voltage of 0.4 kV and, accordingly, a phase voltage of 220 V is used, a wire with a cross section from the minimum value is most often used: 2.5 - aluminum and 1.5 mm.kv. copper. Basically, such standard current conductors are suitable for lighting circuits.
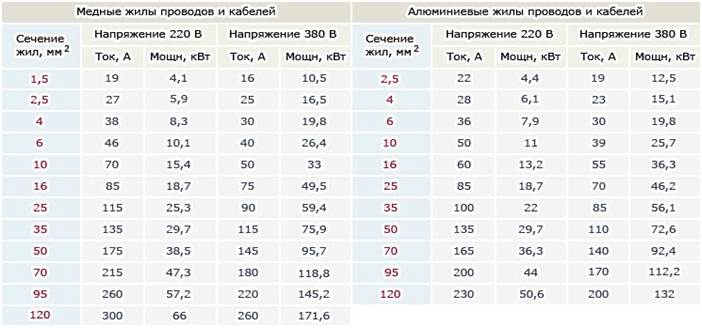
All other sections and, accordingly, their diameters depend on the power and, of course, the current in the circuits of household electrical equipment. To determine the cross-section required for wiring, the table below. Using it, knowing the total power of electrical appliances connected to this network, you can easily find the required core size.
At the same time, it is still recommended to choose a section with a margin slightly, that is, the nearest larger standard value. For example, the voltage in the network is single-phase 220 Volts and the owner of the room has a need to power devices with a capacity of, say, 7 kW. According to the table there is no such power, but there are 5.9 and 8.3 kW. For copper wiring, you need a cable with a cross section of 4 mm2. If the budget is limited and the task is to make aluminum wiring, then the nearest larger parameter indicated in the table will be 7.9 kW, which corresponds to a 6 mm core2.
You can also combine wires of different cross-sections, for example, from the input machine to the junction box more, and then when wiring to groups of electrical consumers or to fixtures occurs, you can lay a smaller wire. The main thing you need to remember about the rules aluminum and copper wiring connections, in case of need.
In the production of electrical equipment, the power is much higher than in everyday life, and the voltage in high-voltage networks is 6 kV, 10 kV, 35 kV, etc. That is why here the standard sections of wires and cables are more diverse. This value is calculated with a large margin, since the main most powerful electric power receivers are electric motors, and during startup they can amplify the current in the power circuits supplying them 5–7 times higher than the nominal one.
However, for the supply of lighting equipment and secondary switching circuits carried out by control cables, the same wires of 1.5–2.5 mm are widely used2 and they are quite enough.
For power circuits of 6 kV, aluminum cable products from 120 mm are often used2. If this cross-section of the cable is not enough, then two lines are connected, connected in parallel to each other, thereby sharing the load on each of them. In everyday life, such methods are inappropriate. For especially powerful equipment, installation of circuits with four or even six parallel conductors is found.
There are cases when, for low-voltage circuits, cables with a rather large cross-section of conductors are necessary, as, for example, in the case of the organization of welding work.
The choice of wire cross-section is very important and individual, therefore, whole design offices or individual companies, which include experienced design engineers, are engaged in this at the production site.
Finally, we recommend watching a useful video on the topic:
We hope that the standard cross-sections of cables and wires, as well as the tables with which you can select the appropriate core size, have helped you fully understand this issue!
It will be useful to read: