What is a cross-module and why is it needed?
Design
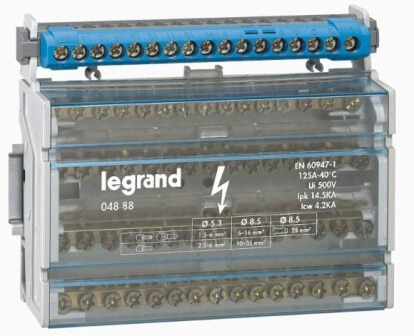
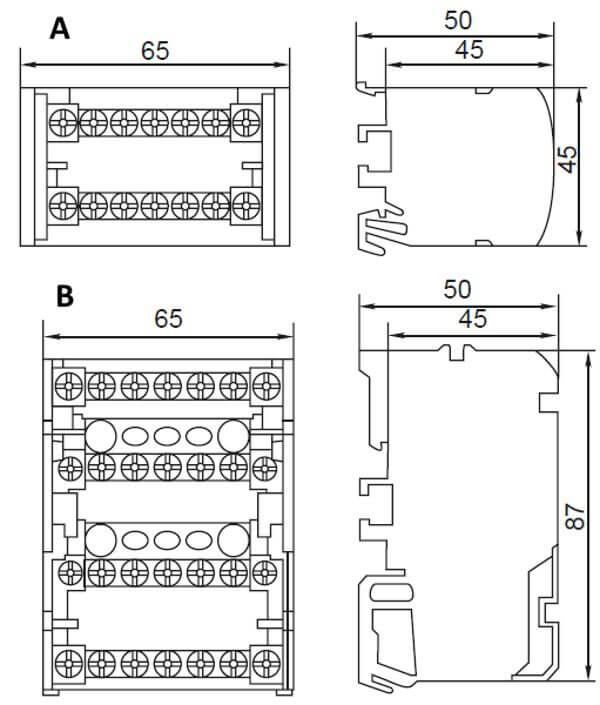
A modular distribution block consists of a certain number of metal busbars that are isolated from each other. The tire fabrication material may be either electrical copper or brass. Also in the design of the cross-module are screw terminals, thanks to which fast and safe switching of wires of various sections is carried out.
The housing of the distribution block itself is made of heat-resistant self-extinguishing plastic, so that such products are considered fireproof. In addition, the cross-module design includes a hinged lid, thanks to which the tires are protected from accidental penetration of foreign objects. The cover is made of transparent plastic, which makes it convenient to revise the distribution panel.
It should also be noted that there are several types of cross-modules: zero (for connecting zero wires), phase and combined. The difference between the zero distribution block and the phase one is that the latter is able to withstand a higher current load due to its design.
In addition to this, products can be unipolar (or as they are also called single-phase) or multipolar (at 2, 3, 4 poles). Multi-pole modular distribution blocks are used for assembly of three-phase switchboards.
As for the technical characteristics, cross-modules can be designed for different current loads: from 80 to 500 A. There are also differences in the sections at the input and output. The input section of the wire can be from 16 to 185 mm2, and the output can have from 2 or more terminal blocks, designed for different, smaller cross-section. In order to choose a suitable embodiment, you must first draw up a distribution board diagram in order to know which wires will be switched.
It should also be noted that there are cross modules designed for switching digital networks: twisted pair or optical fiber. They are called optical cross-modules.
Application area
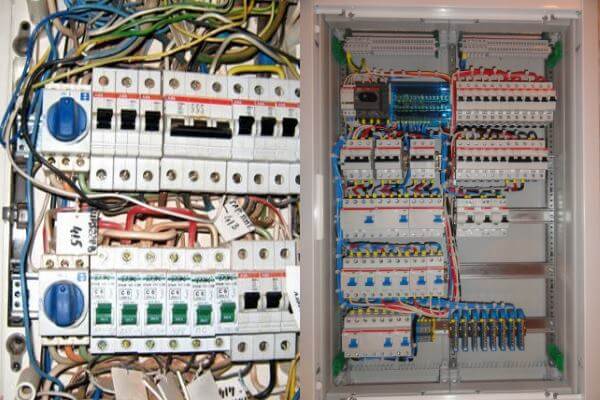
As you already understood, the purpose of the cross-module is to switch wires in the shield. Indeed, a switchboard in which the wires are connected through a special cross module will look much more professional.You can verify this by viewing this photo:
In addition, the use of these products allows you to quickly understand the circuit board, which will speed up repair and electrical work.
Cross-modules are also used during installation. main ground bus. In this case, the distribution block plays the role of a terminal block - it connects the ground wires of a small section to the input.
Connection
Installing and connecting a cross-module is not difficult. The case is quite simple to mount on a din rail, so you can install it very quickly. Wiring is also easy. The video below shows how to connect a cross module, as well as the advantage of its use is clearly demonstrated:
So we examined what a cross-module is, why it is needed and what sizes this product is. Finally, we recommend buying a modular distribution block from trusted manufacturers: ABB, IEK, Legrand, Dekraft or Schneider Electric. The quality of the materials plays a very important role in the operation of this device.
We also recommend that you read:







Thank you