Overview of halogen lamp specifications
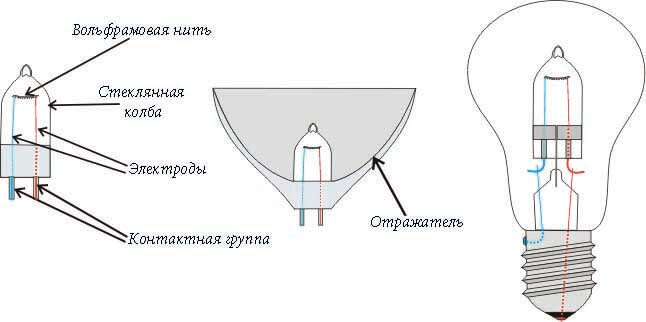
The halogen lamp device has much in common with incandescent lamp, which is installed in almost every residential building. This bulb consists of a bulb, a tungsten filament, electrodes and a group of contacts, as shown in the picture.
The main structural difference between halogen lamps and incandescent lamps is as follows:
- inside the flask are bromine and iodine vapors, instead of an inert gas (or vacuum);
- the material for making the flask is quartz.
These two differences significantly extend the number of working hours of the product, as well as its efficiency (we'll talk about this a bit later).
Characteristic
The main technical characteristics of halogen lamps:
- power range ranges from 1 W to 20 kW;
- rated voltage can be 6/12/24/110/240 V (depending on application conditions);
- the heating temperature of the tungsten filament is about 3000 degrees;
- light output - from 15 to 22 lm / 1 W;
- socle size - 14 mm (E14, Mignon) and 27 mm (E27 standard);
- the service life is from 2000-4000 hours during normal operation (with a smooth start, the mark can reach a record 12000 hours).
Varieties
Today, there are 4 main types of halogen lamps:
- Linear
- With external flask
- With reflector
- Capsule
Let us briefly consider each of the types of products, as well as the pros and cons of each option.
Linear halogen lamps were made in the last century (in the 60s). They have a special design - an oblong cylindrical shape with two socles. Power can reach 20 kW, so they are used both in everyday life and in industrial applications (floodlights). The advantage of these bulbs is their high strength properties and brightness. The disadvantage is increased power consumption.
A halogen lamp with a double bulb (external) is practically no different from the classic version, however, if you look closely, inside the glass shell you can see another small bulb, as shown in the photo. The outer bulb is used to protect the halogen from human contact and mechanical damage. Today, there is a wide range of lamps with an external bulb: matte, milky, decorative, etc. The cap size can be standard (E27) and reduced (E14).
To make the light flux directed, the bulb is coated with an aluminum or infrared reflector. As a result, lighting becomes the most effective because all the light goes to the desired area of the room. Most often, such options are used for installation of concealed ceiling lighting (Spotlights),
There are many varieties of halogen lamps with a reflector: with protective glass, without it, etc. The type of cap is represented by a two-pin contact group of various sizes (the distance between the contacts can be from 3 to 10 mm).
Capsule models have miniature dimensions and relatively low light output. Most often, capsule halogen lamps are used exclusively for decorative purposes, for example, for lighting furniture.
As in the previous version, the base can have several sizes: from 3 to 9 mm between the contacts.
Marking
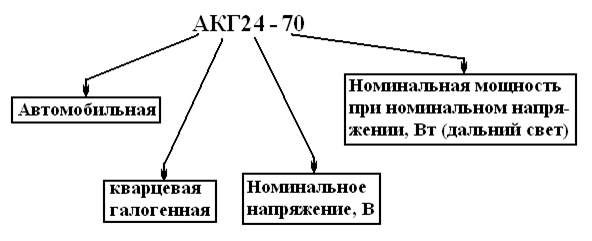
The marking of halogen lamps for the CIS countries is as follows:
- the first letter is the material for making the flask (“K” means quartz);
- the second letter is the name of the gas in the flask (if “G” is halogen, if “I” is iodine);
- the third letter - design features ("M" - small);
- the first group of numbers is the operating voltage in Volts and through hyphen the rated power in Watts;
- the last digit is the product revision number (as opposed to the base model).
Advantage
The advantage of halogen lamps is as follows:
- small dimensions;
- relatively long service life (2 times more than that of incandescent lamps);
- moderate power consumption;
- have increased mechanical strength and heat resistance due to the quartz shell design;
- increased light output;
- luminous flux can be adjusted;
- low cost;
- A wide range of products for various applications.
disadvantages
There are several disadvantages of halogen incandescent lamps:
- It is strictly forbidden to touch the light bulb with your hands, as it can significantly reduce the service life;
- products fail with voltage drops, so for their work you need to spend money on the acquisition surge protection devices;
- The halogen bulb heats up to high temperatures, so you need to take care of the fire safety in advance during installation.
Application area
The scope of halogen is very diverse. Products are widely used in automotive lighting, decorative lighting, street lighting, as well as in photo and video shooting. Very often they are used during installation of lighting in the apartment and house. Also, bulbs can be used as a heating element in a microwave oven and electric stove.
So we examined the main advantages, disadvantages and technical characteristics of halogen lamps. We hope that in the article you have found all the answers to your questions.
Related materials:










Halogens in dryers cannot be replaced with LEDs; they also heat up well
Interesting, thanks for the detailed description. I have Osram halogen lamps, in principle, there are no complaints about them, although everyone advises taking LEDs from the Osram series. I think so far.
Cool and informative article. Previously, I did not understand much what the difference was, but the article described everything in detail. I’m just starting my independent life in a new apartment, now I know which bulbs it is better to put.
Wikipedia says that the temperature of the thread is 3000 Kelvin, not degrees Celsius.
I would also like to know what is the quantitative ratio of the energy emitted by halogen lamps: heat / visible light / IR / UV