What is the danger of voltage dips in the network and how to protect yourself from them
What is a voltage dip
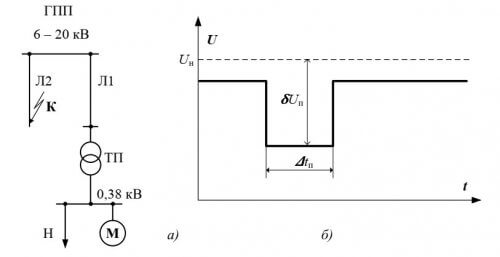
A voltage dip is a sudden decrease in voltage at a point in the electrical network below 0.9 Un, after which the voltage is restored to its original or close level after a period of time from ten milliseconds to several tens of seconds.
Depth and duration are parameters that characterize the voltage dip (relative to the voltage value in normal mode).
The duration of the voltage dip ∆tp is the time interval between the moments: the initial and the moment of voltage recovery to the initial or close to it level.
The magnitude of the voltage dip depth is from 10 to 100%, the duration is from hundredths to several tenths of a second.
The frequency of the occurrence of voltage dips Pn is an auxiliary characteristic and is defined as the number of voltage dips of a certain depth and duration for a certain period of time in relation to the total number of voltage dips for the same period of time.
Causes of Failure
The main reason for the occurrence of voltage dips in the power supply system is short circuits in the branches of the electric network of high (35 ... 220 kV), medium (6 ... 10 kV) voltages and in networks with voltage up to 1 kV that extend from the power supply circuit of this load node.
A voltage dip can happen in the network at any time, and therefore, they are not standardized. But it is necessary to study information about the frequency, depth and duration of voltage dips in the power supply system in order to include uninterruptible power supplies for consumers sensitive to dips in the power supply system. Such consumers are electronic microprocessor control devices, computers, servers and other sensitive devices.
Huge pressure
The inclusion in the electric network of consumers with high electrical power can cause a voltage drop if they cause inrush currents that are several times higher than the rated currents. This is characteristic of engines or incandescent lamps, when turned on, inrush currents can exceed the rated currents by 5-7 times.
A voltage dip can occur if the network is not designed correctly and the switching devices for the equipment are selected incorrectly.To eliminate the influence of inrush currents in the network, modern protective devices are installed that disconnect the voltage in the protected section of the network if the duration of the inrush currents exceeds the permissible one.
One way to solve this problem is to use a specialized frequency converter, with its help, a reduction in the magnitude of the dips is achieved due to the distribution of the additional load. Another additional solution to this problem may be the use of devices, due to which the circuit is powered with less resistance. Nevertheless, it should be noted that this solution is costly.
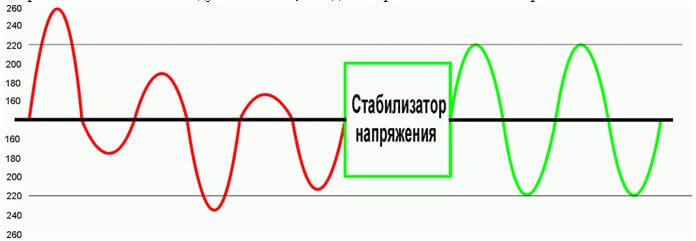
This problem poses a rather serious danger to electric consumers and can lead to bad consequences, for example, burning a motor in an electric device. If the problem of failures could not be solved by the methods described above, then their effect on the devices can be eliminated with the help of stabilizers, electronic regulators, as well as dynamic voltage reducers. It is also important to remember that dips can be in any network, regardless of the voltage class.
Network origin
Distribution of damage over the electrical network is a rather complicated process. From network topology, values load at a specific point of the general connection, as well as the magnitude of the resistance depends on the level of impact of a certain damage on a particular area on other sections of the power grid.
The duration of the resulting failure directly depends on how long the protective system needs to detect and, subsequently, eliminate it. This usually takes a couple of milliseconds. Nevertheless, it should be remembered that there are injuries that are random in nature, for example, if a tree falls on overhead power lines. However, the speed of elimination depends on the nature of the damage and the parameters of the line and protection. If this is a line with an isolated neutral, then with a single-phase earth fault, the damage can be eliminated in up to two hours - for the time of finding the damage by personnel. A two-phase circuit, as a rule, is disconnected in a split second by the action of protection against damage.
In the event of a complete shutdown of a certain area for a sufficiently long time using automation, which serves as protection, all devices located on the site should be completely de-energized until the problem is resolved, the specialists checked and restored the power supply to damaged area. An automatic reclosing device can simplify this situation, and at the same time can contribute to the occurrence of more failures. Auto restart restores power after a time delay in the event of a protective automation. The time delay depends on the power requirements in the electrical network. For responsible consumers, the time delay is a fraction of a second; for other categories of consumers, the time delay can be increased to several seconds.
If the damage is completely eliminated, the equipment is restarted, and the power at the emergency site goes into a stable, normal state. However, if the damage was not repaired during automatic restart, the protective devices are activated and the damaged part of the electric network is de-energized with a minimum delay. To prevent the development of an emergency, the re-inclusion of the de-energized area is allowed only after the identification and repair of the damage.
However, if the damage was not corrected by means of the secondary switching it did not work, then it is necessary to re-enable the protective automation.The repetition of this process will correspond to the number of starts by the user in the program of the automatic rotary switch. It should be borne in mind that with each attempted secondary start-up in all other areas there will be a repeated voltage failure, which means that other users will experience a series of failures.
Protection methods
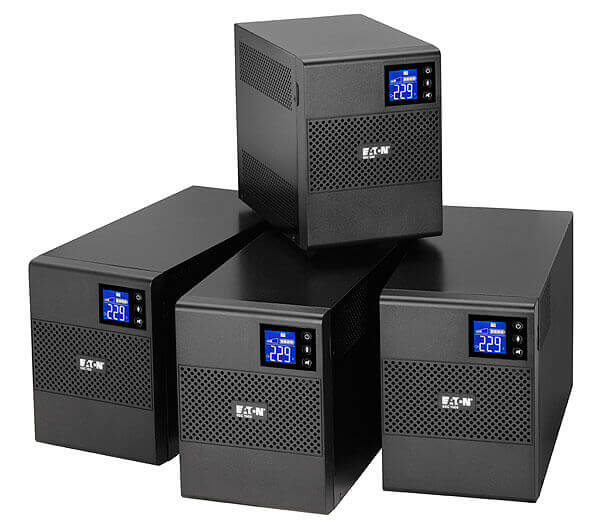
So, you have learned what this phenomenon is, now let's talk about how protection against voltage dips in the network can be organized. If you need to protect a low-power load, it is enough to install an uninterruptible power supply (UPS). Such a solution can be applied even at industrial facilities for emergency folding of technological processes and the safe storage of information.
If you need to protect a powerful load from voltage dips, in this case it is necessary to use specialized systems that carry out dynamic voltage recovery. Such systems are able to compensate for the missing part of the voltage, however, this type of protection works for a short time. That is why they are not able to protect against prolonged voltage dips in the electrical network.
That's all I wanted to tell you about what are the voltage dips in the network, what are the causes of their occurrence and how can you protect the equipment from this phenomenon. It should be noted that computer equipment is the most sensitive to failures. Therefore, if this phenomenon is observed in your network, be sure to protect the electronics using the above methods.
It will be useful to read: