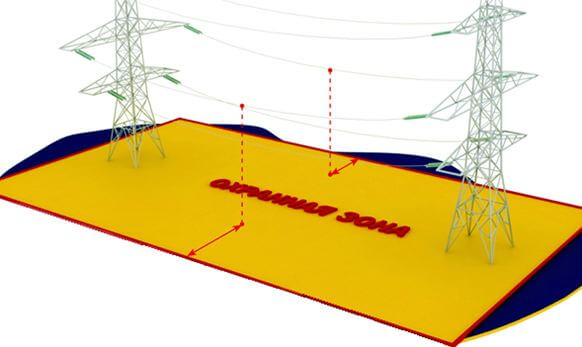
Security zones of power lines
Norms and Rules
Today there is a decree and requirements, according to which a security zone is formed. Over time, these rules have become more stringent and demanding, which is associated with a change in the results of the survey.
Under these rules, the buildings that were operated earlier fell, but they are not taken from the owners. Such buildings can be used, but their sale is allowed with the indication of restrictions, which are mandatory prescribed in the sales document.
There are two main positions, on the basis of which, restrictions are determined:
- Permanent residence in such buildings is prohibited;
- It is forbidden to carry out major repairs inside the building or to build extensions.
Important! In addition, the land, which is located in the protected territory of the power transmission line, is for sale. To find out what restrictions are on it, it is enough to contact the district administration with this question.
Classification of protected areas
The security zones of overhead lines are divided into classes. The differences in the classes are how much power the power line has, as well as how many meters from it to the ground (installation height). This does not include communication wires. What class has a power line can be determined visually. To do this, it is enough to calculate how many hanging wires (namely, how many lived in one phase) and how many fuses are on the poles.
The difference in the number of cores in one phase:
- Transmission lines less than 330 kV (one core);
- 300 kV (two);
- 500 kV (three);
- 750 kV (four).
There is also a classification of protected areas of power lines by the number of fuses that are on poles. In this case, there is a division into 4 classes:
- Power lines below 10 kV (one fuse);
- 35 kV (from three to five fuses);
- 110 kV (six to eight);
- 220 kV (from ten to fifteen fuses).
Sanitary standards
Rules "SanPiN 2971-84. Sanitary standards and rules for protecting the population from the effects of an electric field created by overhead power lines of alternating current of industrial frequency ”sanitary protection zones of power lines are also approved. Classes are divided depending on the power of the transmission line.
The sizes of the plots are determined depending on the distance from the overhead line to the buildings. It does not matter if it is a residential building or a production building.
According to the PUE p. 2.5.216 (see Chapter 2.5) the horizontal distance from the extreme wires of the overhead lines to 220 kV with their greatest deviation to the nearest parts of industrial, warehouse, office and public buildings and structures should be at least: 2 m - for overhead lines up to 20 kV, 4 m - for overhead lines 35 -110 kV, 5 m - for OHL of 150 kV and 6 m - for OHL of 220 kV.
The horizontal distance from the extreme wires of the OHL of 330 kV and above should be at least:
- to the nearest parts of non-production and industrial buildings and structures of power plants and substations with the largest deviation of wires: 8 m - for OHL 330 kV, 10 m - for OHL 500-750 kV;
- to the nearest parts of industrial, warehouse, office buildings and public buildings and structures (except power plants and substations) when the wires are not deflected: 20 m - for overhead lines 330 kV, 30 m - overhead lines 500 kV, 40 m - overhead lines 750 kV .
The passage of overhead lines through the territories of stadiums, educational and children's institutions is not allowed.
In accordance with GOST 12.1.051-90 (Clause 2.1), the distance for lines is the voltage level:
- 20 kV - 10 meters.
- 35 kV - 15 meters.
- 110 kV - 20 meters.
- 150-220 kV - 25 meters.
- 300-500 kV - 30 meters
- 750 kV - 40 meters
- 1150 kV - 55 meters.
If the power line passes through water bodies, the protected area becomes larger, and the minimum distance to the buildings should be from one hundred meters.
Protected Area Installation Procedure
A security zone is defined and established for the entire territory of the network economy. There are several stages of paperwork for the security zone of power lines. The main thing is to fully comply with the border, which is determined and established according to the rules and GOST. The security zone of power lines is established by regional authorities. To confirm it, it is necessary to submit an application to bodies that are directly involved in energy in the region. The application should indicate the territory with the boundaries of the network economy. The application is considered by the authorities up to 15 days.
If the regional authorities have given permission and all issues have been resolved, the following application should be submitted. This time to the federal cadastral authority. This department makes certain changes to the real estate cadastre of the electric grid industry. As soon as all necessary changes have been indicated and recorded in the cadastre, it is considered that the security zone of the power transmission line has been established and entered into force.
Important Nuances
If the power line has a voltage level of 6 to 10 kV, then the following is prohibited in this area.
- planting trees and bushes;
- repair and construction of houses, as well as their dismantling;
- mining, explosions and land reclamation;
- the construction of gas stations;
- the construction of sports grounds and places for children to play;
- events with a large crowd of people;
- construction of warehouses.
All work that is planned to be carried out in this territory must be coordinated with the organization to which this protection zone of the power transmission line belongs. Permission to hold events is granted in writing only.
If the established rules were violated and there was a break in the supply of energy, then you should know the following:
- legal entities must pay a fine of one hundred to two hundred minimum wages;
- individuals must pay between five and ten minimum wages.
Since the power line adversely affects human health, all the rules and regulations have been developed to ensure the safety and organization of dangerous areas protected by the state. These rules are strict, but thanks to them, human safety is ensured. In the end, we recommend watching a video in which the requirements for the size of the protected areas of the power transmission line, as well as the rules for working and staying in them, are examined in detail:
Now you know what the security zones of power lines are, what regulatory documents describe their size and what requirements are presented to protected areas.We hope the information provided was interesting and useful for you!
We also recommend reading: