What is phase, zero, and ground for?
Simple explanation
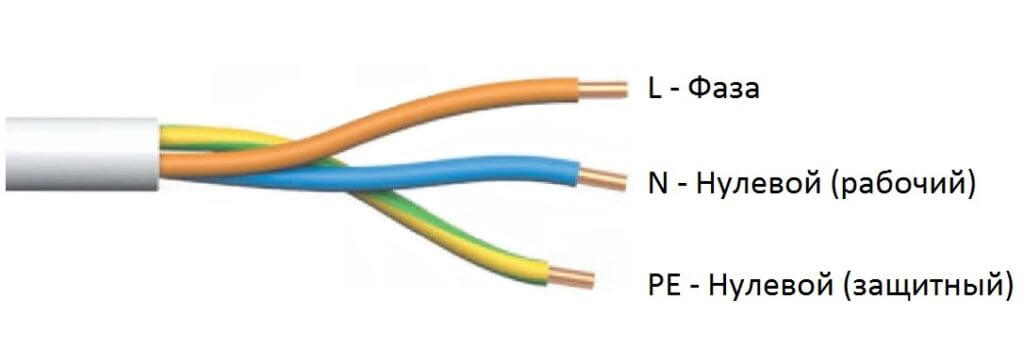
So, for starters, in simple words, we will tell you what the phase and neutral wires are, as well as grounding. A phase is a conductor through which current flows to the consumer. Accordingly, zero serves to ensure that the electric current moves in the opposite direction to the zero circuit. In addition, the purpose of zero in the wiring is to equalize the phase voltage. The ground wire, also called ground, is not energized and is designed to protect a person from electric shock. Read more about grounding You can find out in the corresponding section of the site.
We hope that our simple explanation helped to understand what zero, phase and earth are in electrics. We also recommend that you study color marking wires, to understand what color is the phase, neutral and ground conductor!
We delve into the topic
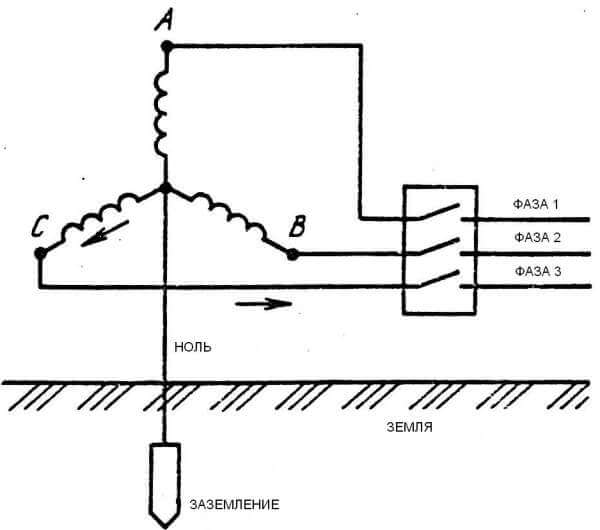
Consumers are powered from the low voltage windings of a step-down transformer, which is an essential component of the operation of a transformer substation. The connection of the substation and subscribers is as follows: a common conductor is supplied to the consumers, departing from the connection point of the transformer windings, called neutral, along with three conductors representing the conclusions of the other ends of the windings. In simple words, each of these three conductors is a phase, and the common one is zero.
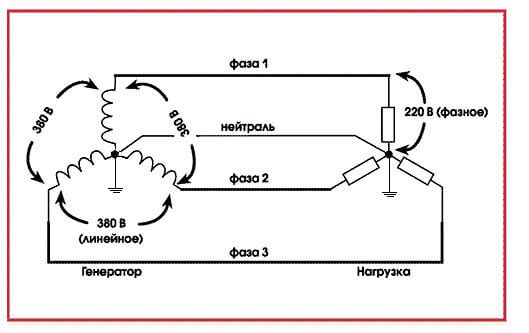
Between phases in a three-phase energy system, a voltage called linear occurs. Its nominal value is 380 V. Let us determine the phase voltage - this is the voltage between zero and one of the phases. The nominal value of the phase voltage is 220 V.
An electric power system in which zero is connected to the ground is called a “system with dead earthed neutral." To make it extremely clear even to a novice in electrical engineering: by "ground" in the electric power industry is meant grounding.
The physical meaning of a grounded neutral is as follows: the windings in the transformer are connected to a "star", while the neutral is grounded. Zero acts as a combined neutral conductor (PEN). This type of connection to the land is typical for residential buildings belonging to the Soviet building. Here, in the porches, the electrical panel on each floor is simply blanked, and a separate connection to the ground is not provided.It is important to know that connecting both the protective and the neutral conductor to the shield body is very dangerous, because there is a possibility of the working current passing through zero and its potential deviating from zero, which means the possibility of electric shock.
For houses belonging to a later construction, from the transformer substation, the same three phases are provided for, as well as a separate neutral and protective conductor. Electric current passes through the working conductor, and the purpose of the protective wire is to connect the conductive parts to the grounding circuit available at the substation. In this case, in the electrical panels on each floor there is a separate bus for separately connecting the phase, zero and ground. The grounding bus has a metal connection with the body of the shield.
It is known that the load among subscribers should be distributed evenly across all phases. However, it is not possible to predict in advance what capacities will be consumed by one or another subscriber. Due to the fact that the load current is different in each individual phase, a neutral bias appears. As a result, a potential difference arises between zero and ground. In the case where the cross section of the neutral conductor is insufficient, the potential difference becomes even more significant. If the connection with the neutral conductor is completely lost, then there is a high probability of emergencies in which the voltage approaches the zero value in phases loaded to the limit, and tends to a value of 380 V in unloaded phases, which leads to a complete breakdown of the electrical equipment . At the same time, the case of electrical equipment is under voltage, dangerous to human health and life. The use of separated neutral and protective wires in this case will help to avoid the occurrence of such accidents and ensure the required level of safety and reliability.
In the end, we recommend watching useful videos on the topic, which give definitions of the concepts of phase, zero and grounding:
We also recommend reading:






"The current moves in the opposite direction to zero" ...
the current in our sockets is alternating, what direction can there be?
all the time he changes directions 50 times per second, why in all articles about phase and zero the explanation begins with this “direction”?
All the same, it’s not very clear even for my 35 years old and work experience as a programmer for 15 years.
Why is a “phase” called a phase?
Why is “zero” called so?
Why in the old apartment buildings did not do grounding?
Zero, because neutral is earthed with us. That is, ideally there should be zero potential on this wire. The phase is called phase, because the output of the generator is three-phase, the power supply system is three-phase, and this is one of them. Zero also leaves the generator when its windings are connected by a star, the connection point is zero.
If you take a separating transformer - 220/220 - there will be no zero on the secondary winding, because they are both “in the air”, that is, neither of them is grounded - this is called isolated neutral, this is used, for example, in crane lighting schemes in production .
In fact, all the houses were grounded, the apartment shields were grounded, in some cases, the bathtubs. But in the apartments there was a two-wire power supply system. There are several reasons:
1. Economic. Laying three wires is more expensive and the work will be performed elementarily longer.
2. There was no such an abundance of powerful and complex household appliances.
3.Did you notice that in old apartments, where old meters still stand, there are two plugs, either ceramic, or one automatic, and the second ceramic with a fuse? From the ancient tree there was a voltage of 127 Volts in the network, then they switched to 220V, but immediately converting all risers and transformer substations is a long, expensive, and not always possible, that's why two phases were introduced into the apartments, and the linear voltage in the 127V network is 220V. I mean, the power supply system was modernized with the growth of consumer demand. Accordingly, the electrical safety requirements changed - SNiPs, PUE, etc.
In a modern apartment there are a lot of powerful electrical appliances when used, which there is a big risk of getting an electric shock, for example, when the phase is broken into the housing.
I still didn’t understand anything, the star, the air is zero but then not zero. Why exactly 380 and not 325 or 360? It seems that we would like to explain for dummies but went to the samovars.
What star is air? 380, because they decided so. Why 220? Because they chose such a voltage standard, because in America 110, and in truth 110 + 0 + 110, are in antiphase. Because, why, and 50 hertz. The star was chosen because it is possible to get 380 between phases in the same line and a root of 3 (1.71) times less - 220 between phase and zero. What do you want to ask? Write clearly, please!
thank you very much
Some explain what phase / zero / earth is; others - how to determine where the phase is, where is zero, where is the earth .... And no one will explain WHY to me to know this when performing electrical installation work at home. I can’t find an explanation, WHY, FOR WHICH “home master” to know where the phase, where zero? What is the practical application of this knowledge? Do I have to observe something and not confuse during installation, and what is the danger? Everyone writes: it is very important to know where the phase is, where is zero. And why, no one explains. Well, then, tomorrow I will withdraw from one outlet to a series of outlets. Or I’ll decide to make a wiring for some lamp under a switch with two / three keys. Do I need to know where the phase is, where is the zero? If necessary, then why, for what? Explain the good people.
Well, look. During the phase, the current runs to zero. For sockets, no matter where you connect the phase, and where to zero. But grounding serves a little for another. Grounding is correctly called - "Protective grounding." In its very understanding, this means that it is required only for the protection of electrical appliances, and of the person himself. To do this, there is an RCD (residual current device). It looks like a normal BA (High-speed automatic), perhaps the only difference is the presence of a button on it (Button T or another Test). Where in the houses there is no grounding, some "craftsmen" make a jumper (let's say on the same outlet) from zero to the point of attachment of the protective conductor. And everything seems to work! Nooooooh ... If suddenly in the circuit of the house itself the phase and zero are suddenly changed (they mix up), then your conductor will become zero and the phase will be zero, and since the craftsman connected zero (jumper) to ground, then your electrical appliances can say " let's goodbye, ”and for one they’ll start to fight with electric shock))))
For example, for the correct connection of the Ilyich bulb. The phase goes through the switch, and zero immediately to the chandelier.
The second figure shows how zero is grounded (in the ground), but where does the zero come from in apartments? That is, only three phase wires are suitable for the apartment panel?