How is the transmission and distribution of electricity
Electricity Transportation Route
So, as we have already said, the starting point is the power plant, which, in fact, generates electricity. Today, the main types of power plants are hydro (hydro), heat (TPP) and nuclear (NPP). In addition, there are solar, wind and geothermal electric. station.
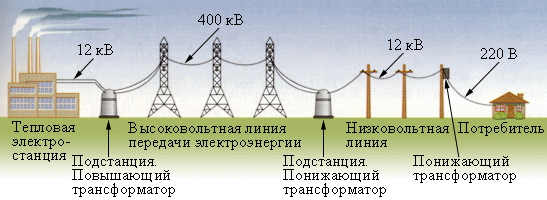
Further from the source, electricity is transmitted to consumers who may be over long distances. To transfer electricity, you need increase voltage using step-up transformers (voltage can increase up to 1150 kV, depending on the distance).
Why is electricity transmitted at high voltage? Everything is very simple. Recall the electric power formula - P = UI, then if you transfer energy to the consumer, then the higher the voltage on the power lines - the less current in the wires, with the same power consumption. Due to this, it is possible to build power lines with high voltage, reducing the cross-section of the wires, compared with power lines with low voltage. This means that construction costs will be reduced - the thinner the wires, the cheaper they are.
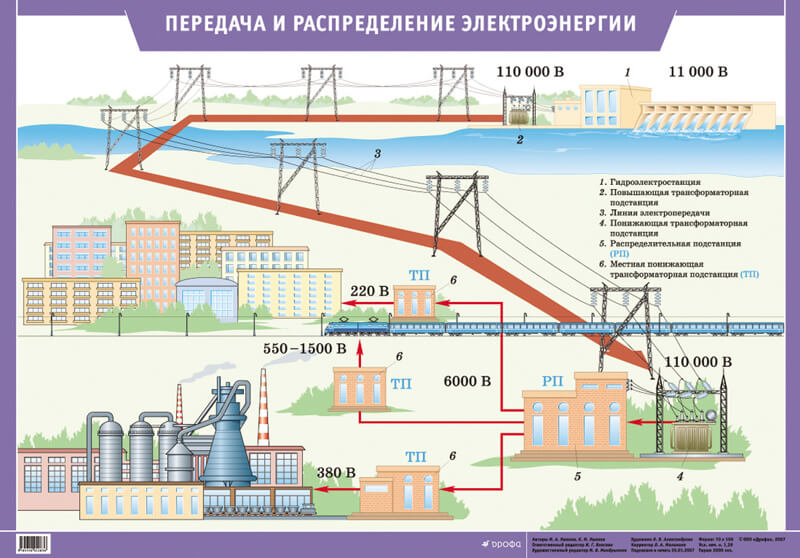
Accordingly, electricity is transferred from the station to a step-up transformer (if necessary), and then with the help of power lines, electricity is transmitted to the central distribution substations (central distribution substations). The latter, in turn, are located in cities or in close proximity to them. On the central circulation undervoltage up to 220 or 110 kV, from where electricity is transferred to substations.
Then the voltage is again lowered (already to 6-10 kV) and the distribution of electrical energy occurs at the transformer points, also called TP. Electricity can be transmitted to transformer points not via power lines, but by an underground cable line, as in urban environments this will be more appropriate. The fact is that the cost of the alienation strip in cities is quite high and it will be more profitable to dig a trench and lay a cable in it than to occupy a place on the surface.
Electricity is transferred from transformer points to multi-storey buildings, private sector buildings, a garage cooperative, etc. We draw your attention to the fact that on the TP the voltage drops again, already to the usual 0.4 kV (380 volt network).
If we briefly consider the route of electricity transmission from a source to consumers, it looks like this: a power plant (for example, 10 kV) - step-up transformer substation (from 110 to 1150 sq) - power transmission line - step-down transformer substation - TP (10-0.4 kV) - residential buildings.
In this way, electricity is transmitted by wire to our house. As you can see, the scheme of transmission and distribution of electricity to consumers is not too complicated, it all depends on how far the distance is.
You can clearly see how electric energy enters the cities and reaches the residential sector, you can in the picture below:
Experts talk in more detail about this issue:
What else is important to know
I also wanted to say a few words about the points that intersect with this issue. Firstly, studies have been conducted for a long time on the topic of how to implement wireless power transmission. There are many ideas, but the most promising solution to date is the use of wireless WI-Fi technology. Scientists from the University of Washington found that this method is quite real and began a more detailed study of the issue.
Secondly, to date, an alternating current is transmitted via a power line, rather than a constant one. This is due to the fact that converting devices that first rectify the current at the input, and then again make it variable at the output, have a rather high cost, which is not economically feasible. However, the throughput of direct current power lines is still 2 times higher, which also makes us think about how it is more profitable to implement it.
So we examined the scheme of transmission of electricity from the source to the house. We hope you understand how electricity is transmitted at a distance to consumers and why high voltage is used for this.
It will be interesting to read:










Want to know why electricity is transmitted at high voltage? Everything is very simple. The fact is that with increasing voltage, the current strength increases,
typo however? or ….
Of course a typo! Sorry, already fixed!